Protein Synthesis Drawing Simple
Introduction to Protein Synthesis
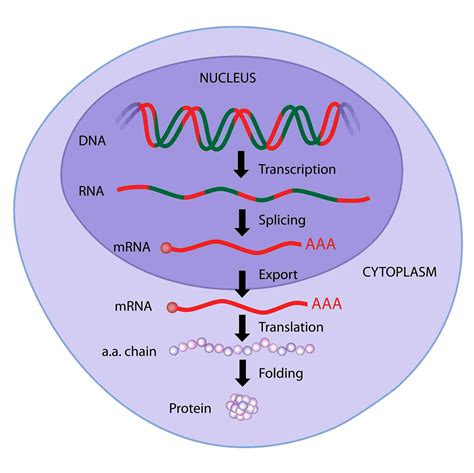
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins, which are essential molecules for various functions in the body, including structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs. It involves the transformation of a DNA sequence into a sequence of amino acids that make up a protein. This complex process can be simplified into several key steps.
Steps of Protein Synthesis
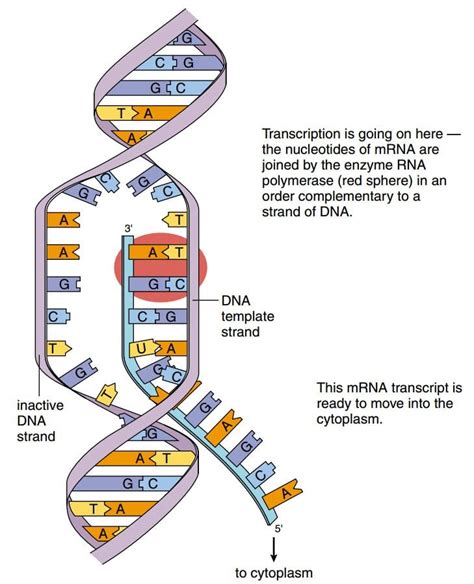
The process of protein synthesis can be broken down into two main stages: transcription and translation. Understanding these stages is crucial for grasping how proteins are made.- Transcription: This is the first step where a particular segment of DNA is copied into a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). The process occurs in the nucleus and is initiated when an enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at a specific region called the promoter. The DNA double helix is unwound, and one of the DNA strands serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary RNA molecule. Once the mRNA is synthesized, it undergoes processing, which includes the addition of a 5’ cap and a poly-A tail, and the removal of introns.
- Translation: After the mRNA molecule is processed, it travels out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. Translation involves the assembly of amino acids into a polypeptide chain based on the sequence of the mRNA. This process takes place on structures called ribosomes, which read the sequence of the mRNA in sets of three nucleotides at a time, known as codons. Each codon specifies one of the 20 amino acids, which are brought to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, it links the amino acids together in a sequence determined by the codons, forming a polypeptide chain. The sequence of amino acids determines the structure and function of the protein.

Key Components Involved in Protein Synthesis
Several key components are involved in the process of protein synthesis, including: - DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid): Provides the template for mRNA synthesis. - mRNA (Messenger RNA): Carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome. - tRNA (Transfer RNA): Brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome based on the codon sequence of the mRNA. - Ribosomes: The site of protein synthesis where mRNA is translated into a polypeptide chain. - Amino Acids: The building blocks of proteins.
Importance of Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is vital for the growth, repair, and maintenance of all living organisms. Proteins perform a wide range of functions, including: - Structural roles: Providing structure to cells and tissues. - Enzymatic activities: Catalyzing biochemical reactions. - Hormonal regulation: Acting as hormones to regulate various bodily functions. - Immune responses: Participating in the immune system to defend against pathogens.🔍 Note: Understanding protein synthesis is crucial for appreciating the complexity and beauty of biological systems, as well as for developing treatments for diseases related to protein dysfunction.

Challenges and Diseases Related to Protein Synthesis
Dysregulation or errors in protein synthesis can lead to various diseases, including genetic disorders, cancers, and neurodegenerative diseases. For instance, mutations in the DNA can lead to the synthesis of aberrant proteins, which can cause disease. Additionally, defects in the protein synthesis machinery itself, such as ribosomal mutations, can also lead to disease.
| Disease | Cause |
|---|---|
| Sickle Cell Anemia | Mutation in the hemoglobin gene leading to abnormal hemoglobin protein |
| Cystic Fibrosis | Mutation in the CFTR gene affecting the synthesis of a chloride channel protein |
| Cancer | Various mutations leading to uncontrolled cell growth and division, often involving proteins that regulate cell cycle |
In conclusion, protein synthesis is a fundamental biological process that underpins the function of all living cells. Through the processes of transcription and translation, cells convert genetic information into proteins, which are essential for structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs. Understanding protein synthesis not only deepens our appreciation for the intricacies of life but also underpins advances in medicine and biotechnology.
What is the role of mRNA in protein synthesis?
+mRNA carries the genetic information copied from DNA to the ribosome, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis.

How do ribosomes read mRNA?
+Ribosomes read mRNA in sets of three nucleotides at a time, known as codons. Each codon specifies one of the 20 amino acids.

What are the consequences of errors in protein synthesis?
+Errors in protein synthesis can lead to the production of abnormal proteins, which can cause diseases. Examples include sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and certain forms of cancer.


