15 Wnt Pathway Alterations: Essential Cancer Research
Introduction to Wnt Pathway Alterations in Cancer
The Wnt signaling pathway is a complex network of proteins that plays a critical role in various cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Alterations in the Wnt pathway have been implicated in the development and progression of various types of cancer. In this blog post, we will discuss the essential aspects of Wnt pathway alterations in cancer research, highlighting the key players, mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets.
Wnt Signaling Pathway: An Overview
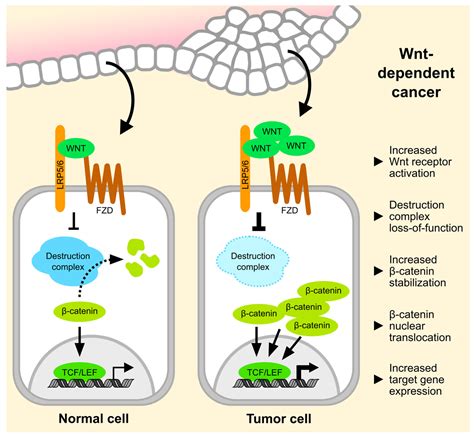
The Wnt signaling pathway is activated when Wnt proteins bind to their receptors, triggering a cascade of downstream events that ultimately lead to the regulation of gene expression. The canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway is the most well-studied branch of the Wnt signaling pathway, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and regulating cell fate decisions. However, dysregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway has been linked to the development of various cancers, including colorectal, breast, and lung cancer.
Key Players in Wnt Pathway Alterations
Several key players are involved in Wnt pathway alterations, including: * Wnt proteins: These proteins are the ligands that activate the Wnt signaling pathway. * Frizzled receptors: These receptors bind to Wnt proteins and trigger the downstream signaling cascade. * β-catenin: This protein is a central component of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway and plays a critical role in regulating gene expression. * APC: This protein is a negative regulator of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and is often mutated in cancer.
Mechanisms of Wnt Pathway Alterations in Cancer
Wnt pathway alterations can occur through various mechanisms, including: * Genetic mutations: Mutations in key components of the Wnt signaling pathway, such as APC or β-catenin, can lead to dysregulation of the pathway. * Epigenetic modifications: Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation or histone modification, can alter the expression of Wnt signaling components. * Protein-protein interactions: Aberrant protein-protein interactions can disrupt the normal functioning of the Wnt signaling pathway.
Wnt Pathway Alterations in Specific Cancers
Wnt pathway alterations have been implicated in various types of cancer, including: * Colorectal cancer: Mutations in the APC gene are common in colorectal cancer and lead to dysregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. * Breast cancer: Alterations in the Wnt signaling pathway have been linked to the development of breast cancer, particularly in the context of estrogen receptor-positive tumors. * Lung cancer: Wnt pathway alterations have been identified in lung cancer, particularly in the context of non-small cell lung cancer.💡 Note: The Wnt signaling pathway is a complex network, and alterations in this pathway can have varying effects depending on the specific cancer type and context.

Potential Therapeutic Targets
The Wnt signaling pathway offers several potential therapeutic targets for cancer treatment, including: * Wnt inhibitors: Small molecule inhibitors that target Wnt proteins or their receptors. * β-catenin inhibitors: Inhibitors that target β-catenin and prevent its interaction with TCF/LEF transcription factors. * APC stabilizers: Compounds that stabilize APC and prevent its degradation, thereby inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
| Therapeutic Target | Description |
|---|---|
| Wnt inhibitors | Small molecule inhibitors that target Wnt proteins or their receptors |
| β-catenin inhibitors | Inhibitors that target β-catenin and prevent its interaction with TCF/LEF transcription factors |
| APC stabilizers | Compounds that stabilize APC and prevent its degradation, thereby inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway |

Future Directions
Further research is needed to fully understand the complex mechanisms of Wnt pathway alterations in cancer and to develop effective therapeutic strategies. Some potential areas of research include: * Investigating the role of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways in cancer development and progression. * Developing combination therapies that target multiple components of the Wnt signaling pathway. * Identifying biomarkers that can predict response to Wnt-targeted therapies.In summary, Wnt pathway alterations play a critical role in the development and progression of various types of cancer. Understanding the key players, mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets involved in Wnt pathway alterations is essential for the development of effective cancer therapies. By continuing to investigate the complex mechanisms of Wnt signaling in cancer, we can uncover new opportunities for targeted therapies and improve patient outcomes.

What is the role of the Wnt signaling pathway in cancer?
+
The Wnt signaling pathway plays a critical role in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, and alterations in this pathway have been implicated in the development and progression of various types of cancer.

What are the key players involved in Wnt pathway alterations?
+
The key players involved in Wnt pathway alterations include Wnt proteins, Frizzled receptors, β-catenin, and APC.

What are the potential therapeutic targets for Wnt pathway alterations?
+
The potential therapeutic targets for Wnt pathway alterations include Wnt inhibitors, β-catenin inhibitors, and APC stabilizers.



